Export Documentation & Procedures: Simplified Guidelines
Export Documentation and Procedures: A Comprehensive Overview
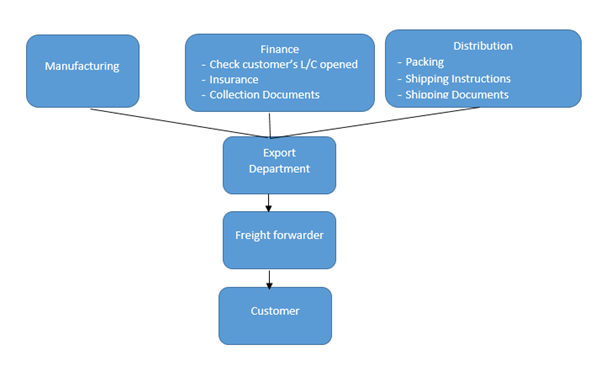
Exporters often rely on freight forwarders to manage the extensive documentation required for international trade. Below are the key documents commonly used in exporting, along with a step-by-step guide to export procedures:
Common Export Documents:
- Commercial Invoice
- Bill of Lading
- Consular Invoice
- Certificate of Origin
- Inspection Certification
- Dock Receipt and Warehouse Receipt
- Destination Control Statement
- Insurance Certificate
- Export License
- Export Packing List
Export Procedures:
Step 1: Enquiry:
- Export transactions typically begin with an enquiry from the buyer, specifying details such as product requirements, quantity, delivery schedule, and terms of payment.
Step 2: Proforma Generation:
- Upon receiving the enquiry, the exporter provides a Proforma Invoice to the buyer, outlining the terms of the offer.
Step 3: Order Placement:
- If the offer is accepted, the buyer places an order on the exporter, providing specifications and quantity requirements.
Step 4: Order Acceptance:
- The exporter acknowledges receipt of the order and commits to the agreed delivery schedule.
Step 5: Goods Readiness & Documentation:
- Once the goods are ready, the exporter prepares the commercial invoice and packing list. Excise duty and sales tax are exempt for export goods.
Step 6: Goods Removal from Works:
- Export consignments are removed following prescribed procedures, with seals by Central Excise authorities to avoid open inspection at the port.
Step 7: Documents for C & F Agent:
- The exporter provides necessary documents to the Clearing & Forwarding Agents, including the invoice, packing list, and declaration forms.
Step 8: Customs Clearance:
- Customs assesses the shipping bill and permits export consignments for ultimate export, endorsing the ‘LET EXPORT’ on the shipping bill.
Step 9: Document Forwarding:
- After completing shipment formalities, C & F Agents forward customs-signed export documents, including the bill of lading or airway bill, to the exporter.
Step 10: Bills Negotiation:
- Exporters negotiate export bills through authorized dealers of Reserve Bank, based on payment terms agreed with the importer.
Step 11: Bank to Bank Documents Forwarding:
- The negotiating bank forwards shipping documents to the importer’s bank to facilitate clearance of the consignment.
Step 12: Customs Obligation Discharge:
- Exporters provide proof of export to Central Excise authorities based on Customs endorsements, ensuring discharge of customs obligations.
Step 13: Receipt of Bank Certificate:
- Authorized dealers issue Bank Certificates to exporters upon receipt of payment, marking the completion of the export transaction.
Key Points:
- Freight forwarders specialize in managing export documentation.
- Export procedures involve multiple steps, from enquiry to receipt of payment.
- Proper documentation and compliance with customs regulations are essential for successful export transactions.
Understanding export procedures and documentation is critical for exporters to ensure smooth customs clearance and compliance with export regulations.